Definition and causes
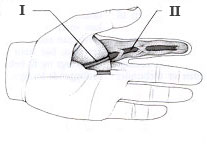
In: Tendon
II: Tendon Sheath
The tendon sheath surrounds certain long
tendons and facilitates the smooth transfer of
the tendon along the skeletal bones.
The tendons are the structures that connect the muscles to the bones. The tendons are strong, flexible but inelastic. Tendons around arms and legs might be long and are used by the muscles as a roping device to move the limbs. The tendons running along the hand and feet joints are surrounded by a sheath which protect the tendon against the underlying bone and which is lined with a mucous membrane which allows the tendon to move smoothly along the bones. The sheath lining might be aggravated causing inflammation and this condition is called tenovaginitis, but there is no infection with bacteria involved. Other tendons in the body are also covered by sheath but without the mucous membrane and also here inflammation might arise which is called tenosynovitis. Inflammation in the tendon itself is tendinitis. (see: Tendinitis) When tendon sheath, or its lining, is aggravated and becomes inflamed and swelling will occur. This limits the space for the tendon and its function is reduced. If this condition continues for too long the sheath may form scar tissue and shrink resulting in permanent reduction of the tendon’s function. Some diseases, such as arthritis and Bechterews disease, increase the risk of tenovaginitis, tenosynovitis and tendinitis. Some people may be hereditary predisposed to tendon disorders.
Symptoms of Tenosynovitis and Tenovaginitis
The symptoms appear as:
-
Pain which is present at rest, but sharply exacerbated by the use of the tendon.
-
Narrowing of the tendon sheath. If the condition affects the sheath of one of the tendons that bends a finger the patient might experience that the tendon suddenly gives way when stretching the finger. This is called a trigger finger and arises because the tendon gets stuck in the narrowed passage and then suddenly releases and the finger stretches with a snap.
-
Tenderness when pressing or squeezing the tendon.
-
Swelling around the tendon.
-
Crackling sounds may be heard, after the condition has healed caused by scar tissue in the tendon sheath.
Precautions and diagnosis of Tenosynovitis and Tenovaginitis
If there is pain when using the muscles and tendons of the hand or ankle joints, it is important to give the tendons rest to heal before resuming the activity which caused the pain. If pain and swelling arises during rest a doctor should be contacted. The diagnosis is made by the physician based on nature of the condition and the typical symptoms. In some cases it might be necessary to perform an ultrasound scan of the affected area.
Treatment of Tenosynovitis and Tenovaginitis
Treatment consists of complete rest and possibly applying a splint to support the tendon. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NAID’s), also used for arthritis patients, may be prescribed by the doctor to relieve pain and swelling. In severe cases, or if the NAID treatment is ineffective, the treatment might be the injection of adrenal cortical hormones (steroid) into the tissues around the tendon. If there is scar tissue which obstructs the tendon mobility surgery might be necessary to make room for the tendon to move freely.
Outlook and complications of Tenosynovitis and Tenovaginitis
The vast majority of cases will subside and disappear by giving the tendon complete rest. However, there is great risk that the condition flares up with the resumption of the same movement patterns which caused the injury. If untreated the condition may lead to the tendon becoming permanently shortened, resulting in a reduced function as for example in a finger. If swelling becomes too great there might be symptoms of compression in the cavities where the tendons and nerves run to the hand and the feet. ( See: Carpal tunnel syndrome). Læs denne artikel på dansk |